import re
import xlrd
def replace_words(text, word_dic):
"""
take a text and replace words that match a key in a dictionary with
the associated value, return the changed text
"""
rc = re.compile('|'.join(map(re.escape, word_dic)))
def translate(match):
return word_dic[match.group(0)]
return rc.sub(translate, text)
"""
preparing the Excel workbook
"""
workbook = xlrd.open_workbook('Book1.xlsx')
worksheet = workbook.sheet_by_name('Sheet1')
num_rows = worksheet.nrows -1
curr_row = 1
while curr_row < num_rows:
curr_row += 1
row = worksheet.row(curr_row)
"""
seting up the cell
"""
hostname = row[0].value
loopback0 = row[1].value
ip_address = row[2].value
netmask = row[3].value
"""
preparing the tamplate
"""
t = open('Template1.txt')
tempstr = t.read()
t.close
values = {
'[Hostname]':hostname,
'[Loopback0]':loopback0,
'[IP_Address]':ip_address,
'[Netmask]':netmask,
}
"""
seting up the output script name,
replace the variable in template with data, then write it out ...
"""
outputfile = hostname + "_CONFIG.txt"
output = replace_words(tempstr, values)
fout = open(outputfile, "w")
fout.write(output)
fout.close
Example excerpt from Cisco configuration script, note the bold text that will be replace by script:
version 12.4
service timestamps debug datetime msec
service timestamps log datetime msec
no service password-encryption
!
hostname [Hostname]
ip cef
!
interface Loopback0
ip address [Loopback0] 255.255.255.0
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/0
ip address [IP_Address] [Netmask]
duplex auto
speed auto
!
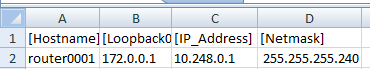 |
| Example data IP |
where:
-Book1.xlsx is our database
-Template1.txt is our template
Get exercise file here.
I hope you found it useful :)